Coined by science fiction author Neal Stephenson in his 1992 novel Snow Crash, the term “metaverse” gained widespread recognition when Facebook rebranded itself as Meta in late 2021.
Opinions on the metaverse vary widely. While some people express concerns about potential threats and the challenges of regulating this digital landscape, others see it as the future of humanity – with approximately 80% of individuals reporting feeling more included in the metaverse than in their everyday lives.
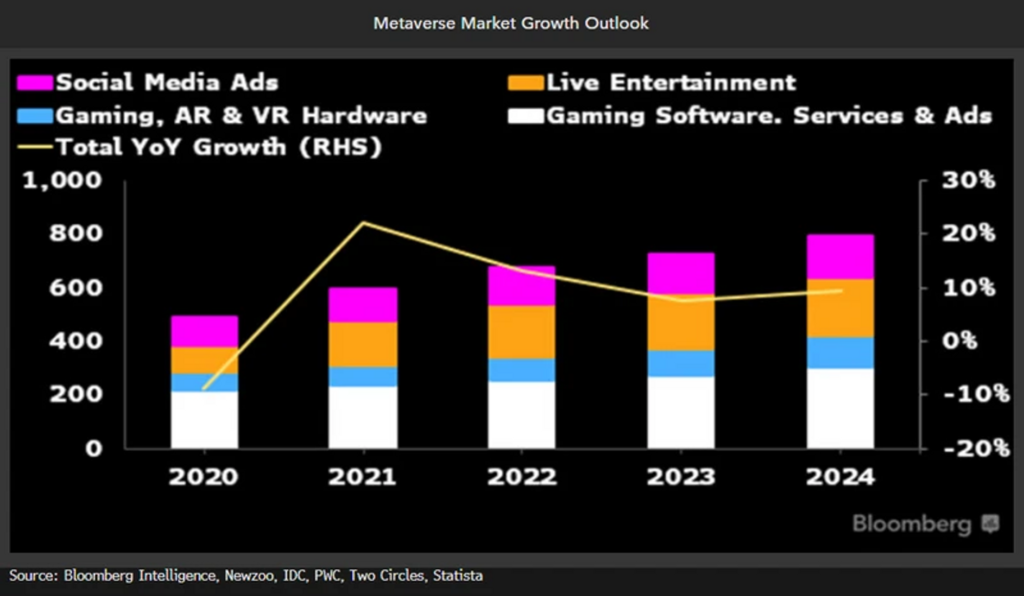
Many media and entertainment sectors have placed great importance on its development, recognizing the impact of the metaverse. More importantly, governments worldwide have begun expressing interest in the metaverse, primarily due to its potential as an economic powerhouse. Now, let’s look at some countries where governmental bodies have displayed a strong interest in the metaverse.
1. South Korea

It is no surprise that South Korea is making significant investments in the metaverse, considering its strong affinity for technology. With ~98% of the population owning a smart device and over 10% involved in cryptocurrency, South Korea stands as a tech-savvy nation.
The country has been actively expanding its metaverse initiatives as part of its “Digital New Deal” political agenda. In February 2022, South Korea announced plans to allocate around $200 million for funding metaverse projects. This initiative aims to elevate South Korea’s position from 12th to 5th among the most metaverse-adopting countries in the world by 2026. According to the Korea Herald, experts predict that the domestic metaverse market in South Korea will be worth 400 trillion won ($306.5 billion) by that time.
In January 2023, South Korea took its metaverse strategy to new heights by unveiling a virtual version of Seoul in the metaverse. The Mayor of Seoul introduced the Meta Seoul project, making Seoul the first city to enter the metaverse.
This platform enables users to access various resources and public services within a virtual reality landscape. Users can explore attractions, access information, consult professionals, file complaints, and engage with other community members. The initial phase of the metaverse project reportedly required an investment of approximately 2 billion won ($1.6 million) from the city government.
Additionally, the Minister of Science and ICT for Seoul expressed plans to support local firms in developing their own metaverse platforms in the coming years. The government also intends to update regulatory IT systems to align with metaverse requirements.
The government allocated 24 billion Korean won ($18.1 million) to establish a fund exceeding 40 billion Korean won ($30.2 million) for metaverse development, as stated in the official announcement. These investments reflect South Korea’s strong belief in the potential of the metaverse and its commitment to becoming a leading player in this rapidly evolving digital landscape.
2. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
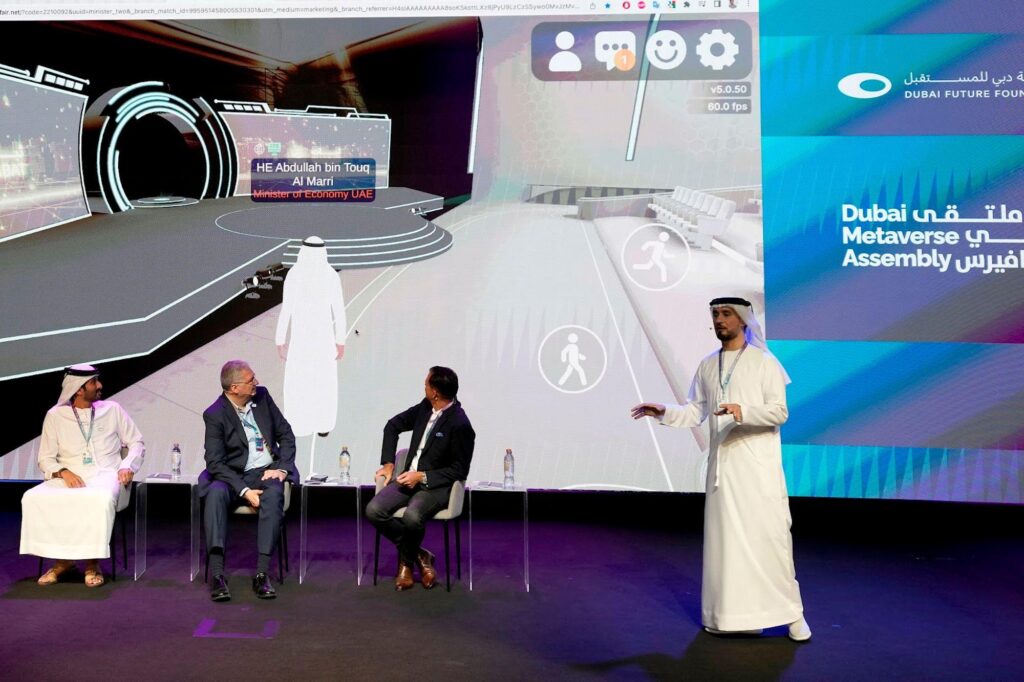

The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is positioning itself as a trailblazer in the metaverse, with ambitious plans to lead the way in this immersive virtual world. In October 2022, the UAE’s economy ministry announced the establishment of its presence in the metaverse, launching the project at Dubai’s gleaming Museum of the Future.
In July 2022, the UAE government unveiled the Dubai Metaverse Strategy, aiming to transform Dubai into one of the top 10 metaverse economies globally. The strategy also aims to position Dubai as a global hub for the metaverse community, with plans to create 40,000 jobs and contribute $4 billion to the emirate’s economy over the next five years.
The following month, the UAE hosted the Dubai Metaverse Assembly, where the Minister of State for AI and the Digital Economy, Omar Al-Olama, announced the country’s intention to introduce a metric called the “gross metaverse product.” This metric will showcase the future ways in which metaverse technology will contribute to the UAE’s economy.
The UAE has also achieved several metaverse world firsts. The Ministry of Health and Prevention (MoHAP) unveiled the world’s first VR customer happiness service center at Arab Health 2022. Furthermore, the Yas Island Metaverse initiative, announced in late 2022, aims to bring Abu Dhabi’s renowned Yas Island, home to the Formula 1 racetrack and the world’s fastest rollercoaster, into the metaverse, marking the first phase of the UAE capital’s presence in the virtual world.
In late 2022, the DEWAVerse platform, launched by the Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA), became the first local government organization to establish its platform in the metaverse, providing services to customers, employees, and the broader society. Besides, Dubai Airport Freezone (DAFZ), part of the Dubai Integrated Economic Zones Authority (DIEZ), introduced METADAFZ in October 2022, offering a seamless digital experience in the metaverse to the free zone’s clients.
The UAE continues to set world records in metaverse adoption. The Dubai Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA) became the world’s first regulator to invest in the metaverse, acquiring a plot of land in The Sandbox to establish its virtual headquarters. In May 2022, the Ajman Police became the first police force worldwide to offer services in the metaverse, training officers to utilize metaverse technology and pilot virtual reality glasses and headsets for customer interactions.
The ADGM Arbitration Centre in Abu Dhabi also launched the world’s first Mediation in the Metaverse service, providing a unique digitized hearing facility for arbitration and mediation, serving the international dispute resolution community. With these groundbreaking initiatives and investments, the UAE is positioning itself at the forefront of metaverse innovation, solidifying its reputation as a pioneer in the virtual realm.
3. Japan

Japan’s government has also shown a positive stance towards the metaverse, recognizing its potential for economic growth. Prime Minister Fumio Kishida made metaverse development a key component of the country’s economic revival plan upon taking office in 2021.
Japan has been actively fostering a digital future by encouraging gaming and animation investments and leading the global Web3 initiative. In July 2022, the Kishida administration established the Web3 Policy Promotion Office, bringing together relevant ministry departments to coordinate efforts. This policy focuses on user protection, security advancements, and implementing regulations requiring crypto exchanges to provide user data.
In October 2022, Prime Minister Kishida announced that Japan would invest in digital transformation services, including non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and the metaverse. Subsequently, in November 2022, the country’s Digital Ministry unveiled plans to create a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) to facilitate government agencies’ entry into Web3.
Besides, ten major Japanese technology and finance giants, such as Mitsubishi and Fujitsu, joined forces to establish a new Metaverse economic zone. This collaboration aims to build an open metaverse infrastructure called “Ryugukoku,” which will drive the next wave of metaverse development. The infrastructure will enable platform interoperability, providing users and developers with versatile tools. Moreover, it will serve as a new social infrastructure for enterprise digital transformation.
In April 2023, a government white paper on Web3 developments, including the metaverse, highlighted the opportunities for remote work in virtual reality, which could help reintegrate socially isolated individuals into the workforce. Japan has an estimated 1.5 million “hikikomori,” individuals who have been socially isolated for at least six months.
The metaverse is also influencing Japan’s recruitment and job-search landscape. Over 2,000 students participated in a metaverse job fair, where they connected with recruiters through virtual avatars and explored various career options while weighing their benefits and drawbacks.
Participants reportedly appreciated the anonymity provided by the metaverse, allowing them to express concerns about employment opportunities. Neo Career Co. managed the employment-related tasks, while X Inc. handled the metaverse-related aspects of this project, which involved 179 organizations.
The Japanese government’s active promotion and investment in the metaverse industry demonstrate its commitment to harnessing the potential of this digital landscape for economic growth and societal development.
4. China
The Chinese government also recognizes the potential benefits of the metaverse for the country’s development and has taken significant steps to promote its growth.In December 2021, China’s Central Commission for Discipline Inspection, responsible for investigating corruption within the Communist Party, published the state’s official definition of the metaverse.
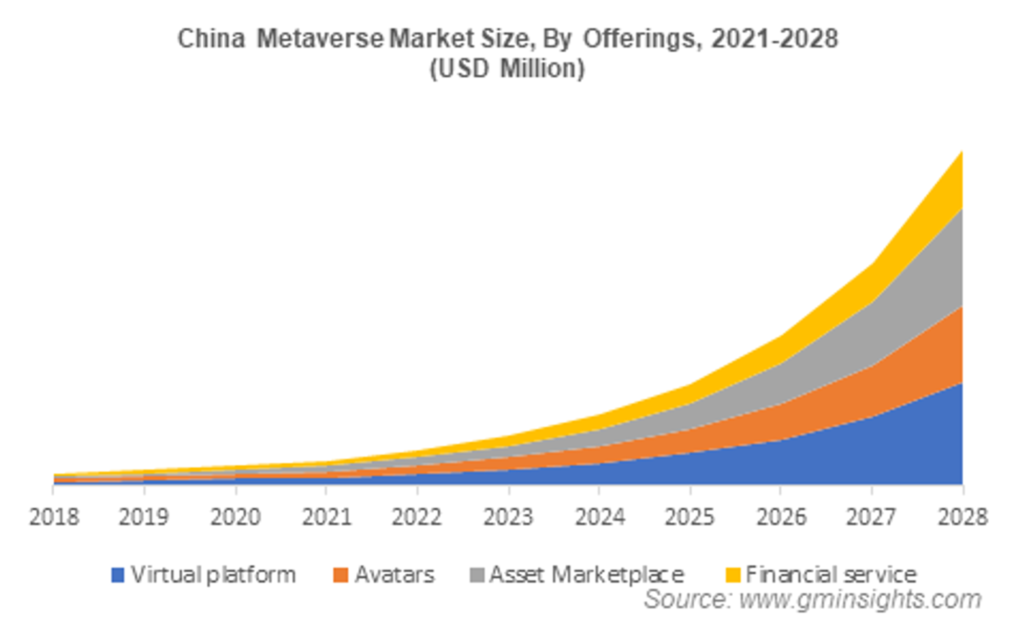
According to the report, the metaverse comprises three key technologies: digital twins, mixed reality, and blockchain. Moreover, Beijing’s 14th Five-Year Plan, a comprehensive economic strategy document guiding national development from 2021 to 2025, included Digital twins.
In fact, an action plan released by five ministries, including the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, sets a target of growing the virtual reality industry to 350 billion yuan ($51 billion).
Breaking new ground, in February 2022, the China National Tourism Administration announced plans to build a metaverse theme park based on Beijing’s Temple of Heaven complex. It demonstrates the Chinese government’s substantial investments in the metaverse and its commitment to leveraging this technology for the country’s overall development across various industries.
Notably, the Government of the City of Shanghai, in 2022, proposed an ambitious initiative to establish a $50 billion metaverse economy. The plan aims to attract ten leading metaverse enterprises and support 100 companies involved in metaverse-related innovations. Although it didn’t disclose the specific investment details, the proposal emphasizes the allocation of special funds to support metaverse companies, indicating Shanghai’s determination to become a thriving hub for metaverse startups.
The city envisions the metaverse industry in Shanghai generating an annual revenue of 350 billion yuan ($49.6 billion) by 2025. To showcase its metaverse potential, Shanghai has presented a collection of 20 initial use cases, ranging from virtual healthcare diagnoses to digital recreations of the city’s historic architectural landmarks.
In February 2023, Nanjing, the capital city of Jiangsu province, unveiled its metaverse strategy, setting ambitious revenue goals exceeding 135 billion yuan ($19.13 billion) by the end of 2025. The city also inaugurated the China Metaverse Technology and Application Innovation Platform in May 2023. This platform aims to advance metaverse research and development throughout the country, reflecting the competitive drive among Chinese cities to establish themselves as key players in the metaverse industry.
While China maintains strict regulations on cryptocurrencies and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), it acknowledges the transformative power of Web3 technologies, including the metaverse, in fueling its digital economy. Former Deputy Minister of the Ministry of Science and Technology, Wu Zhong-ze, emphasized the importance of expanding metaverse applications across various sectors such as education, commerce, healthcare, and entertainment in a recent report.
China’s proactive approach and significant investments in the metaverse indicate its determination to harness the potential of this technology for national development, creating a thriving ecosystem of metaverse-driven innovation and economic growth.
5. Barbados
While not typically associated with the metaverse, Barbados is a forward-thinking country committed to embracing cutting-edge technologies.
The Worlds First Metaverse Embassy? 🧐
— CoinMarketCap (@CoinMarketCap) December 24, 2021
Gabriel Abed, Ambassador of #Barbados 🇧🇧 Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade is looking at putting Barbados Government Embassy on the #Metaverse.
It is set to launch in January 2022.
Full details 👇https://t.co/Tj9zAlh3GF pic.twitter.com/QzkyUuUKYx
In November 2021, Barbados’ Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Foreign Trade made a significant move by signing an agreement with Decentraland to establish a diplomatic embassy within the metaverse. While the initial agreement focuses on Decentraland, Barbados’ government also plans to open virtual embassies in other virtual environments.
As the world’s first embassy within the metaverse, the Barbados embassy sets a precedent that may inspire governments worldwide to follow suit. Like South Korea, countries with virtual embassies can explore innovative ways of engaging and serving their communities within the digital realm.
By embracing the metaverse, Barbados showcases its commitment to shaping the future of digital diplomacy.
6. European Union (EU)
The European Union (EU) recognizes the metaverse as a futuristic digital world and has taken steps to develop comprehensive regulations for its governance. In the State of the European Union address in 2022, an initiative on virtual worlds, including the metaverse, was promised for 2023. Commissioner for the Internal Market, Thiery Breton, confirmed the EU’s focus on the metaverse.
Subsequently, the European Parliament established the Virtual and Augmented Reality Industrial Coalition to facilitate stakeholder dialogue. They also authorized a report on “Virtual Worlds: opportunities, risks, and policy implications for the Single Market.” Additionally, the European Commission organized a citizen’s panel to engage in discussions and contribute to future proposals on virtual worlds.
Interestingly, during his reelection campaign, French President Emmanuel Macron leveraged the metaverse by creating Macronverse, a Minecraft server with a town square, billboard, cafes, a voter registration portal, and a real-life merchandise store.
Germany stands out as a crypto-friendly country with no taxes on long-term capital gains. Berlin has emerged as a blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi) startup hub. In July 2021, Germany passed the Fund Location Act, allowing institutional funds to invest up to 20% of their assets in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
The UK government established the Department of Science, Innovation, and Technology to drive the country’s advancements in the metaverse and Web3 platforms. The department aims to attract investments that will foster these technologies’ economic, business, and developmental benefits.
The UK Prime Minister, Rishi Sunak, has expressed his ambition to establish the country as a crypto hub. Significant funding, including £39.3 million, has already been invested in immersive reality, and the government plans to provide further funding to promote development in science, technology, finance, and other fields. These efforts within the European Union and its member states demonstrate the simple fact that the metaverse is here to stay.
Conclusion
Metaverse has gained significant attention and interest from countries around the world. We have explored the efforts of various nations in embracing and investing in the metaverse, recognizing its potential for economic growth, technological advancement, and societal transformation.
Each country’s approach to the metaverse reflects its unique priorities, ranging from economic development and innovation to social engagement and digital transformation. The ongoing efforts and investments by governments worldwide highlight the metaverse’s role as a catalyst for technological progress, economic growth, and enhanced experiences in various aspects of life.
No doubt, the future of the metaverse is shaped not only by technological advancements but also by the collective efforts of governments, businesses, and individuals to navigate its possibilities responsibly and inclusively.
Interested in more about the metaverse? Check out these articles here.




